Nuclear energy is the energy released by atomic reactions. In nuclear power plants, atoms are split (fission) or combined (fusion) to produce heat, which generates steam that turns turbines to produce electricity through mechanical energy. It is a powerful energy that does not produce greenhouse gases, but it does carry significant risks of other types of waste.
The great advantages of nuclear energy are that compared to other energy sources, nuclear energy does not produce carbon emissions, making it the energy of the future. It has a high efficiency because with a small amount of fuel, it can produce a large amount of energy. And since it does not depend on external or climatic conditions, it is completely self-sufficient, providing a constant and reliable supply of electricity.
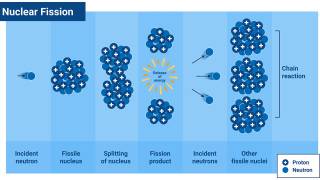
The danger of nuclear energy is radioactive waste and by-products of nuclear reactions that remain dangerous for thousands of years. The safe management and storage of this waste is one of the biggest problems. Accidents such as Chernobyl and Fukushima have shown that the consequences of failures can be catastrophic, even though nuclear power plants are designed with multiple safety systems. These plants are very expensive to build and require significant investment and time.
In conclusion, there are some ways to mitigate the risks associated with nuclear energy, although they cannot be completely eliminated.
Advanced technology should be used, designed with passive and active safety systems that improve operational safety.
Following strict safety protocols and waste management and long-term storage, such as deep geological repositories, can help manage radioactive waste more safely.
The nuclear energy paradox offers a solution to our energy and climate crisis, but it brings with it very serious dangers and challenges, such as accepting to store radioactive waste underground for thousands of years, without knowing if or how it can affect us, since it is not known and cannot be controlled.
It is necessary to improve security measures, develop and regulate waste management. In short, nuclear energy is not a solution, it requires a permanent debate and is of vital importance for the sustainable future we want. The study on fusion energy suggests that in the long term this energy can offer a safer alternative with less waste compared to nuclear fission.
Because it generates significantly less radioactive waste, and the waste generated is less dangerous and has shorter half-lives.
In short, nuclear fusion promises to be a cleaner and more sustainable source of energy in the long term, if we can study and understand the challenges to make it viable.





